Table of Contents
Hey hi all, I got something useful for all web3 learners. Past few days I spent to understand bits and bytes of the Uniswap Protocol. I gathered the best resources to learn all the things about Uniswap V2. During my learning I have taken notes of every thing that I learned. In this post you can get an gist of Uniswap DEX Protocol. You can check my Uniswap V2 Complete Code Walkthrough post to learn everything about Uniswap V2.
Uniswap
Uniswap is an automated ethereum-based crypto exchange with its own governance token, UNI.
Uniswap V1
It introduced the ETH/ERC20 liquidity pool, where LPs (Liquidity Providers) could deposit tokens in exchange for liquidity tokens.
Uniswap V1 uses the X * Y = K constant product equation to calculate token price where
X is the amount of token 1,
Y is the amount of token 2, and
K is the constant that the liquidity pool’s smart contract keeps the same throughout swaps.
Uniswap V1 model faces many issues involving slippage - the change in price of a token because of your trade, and a lack of dedicated token-only pools that forces users to interact with two pools to trade between non-native tokens.
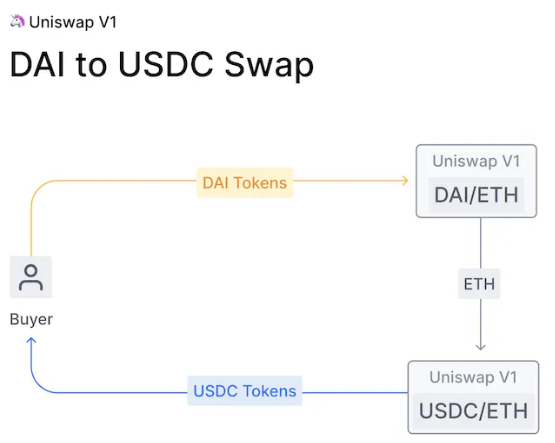
First, the buyer interacts with the DAI/ETH pool to swap his DAI for ETH, then uses that ETH to interact with the USDC/ETH pool which outputs USDC in exchange for the ETH.
Uniswap V1 has a flat 0.3% fee for LPs (Liquidity Providers) to incentivize participation in the network, which must be taken into account as well in the equation.
Weakness :
- Uniswap V1 model faces is the weakness to price manipulation like front-running and sandwich attacks
Uniswap V2
The Uniswap V2 was launched in May, 2020 with a plethora of new features including TWAP (Time Weighted Average Price), Liquidity pools for non-native tokens which halves gas fees and slippage for token swaps, and Flash Swaps. In addition, this update removed native token functionality in favor of WETH (Wrapped Ether) and is written in Solidity - a welcome change for readability.
The 0.3% fee model was shortly modified after release by members of the DAO, where 0.05% of the fee’s funds are reserved for the development of the Uniswap network.
TWAP
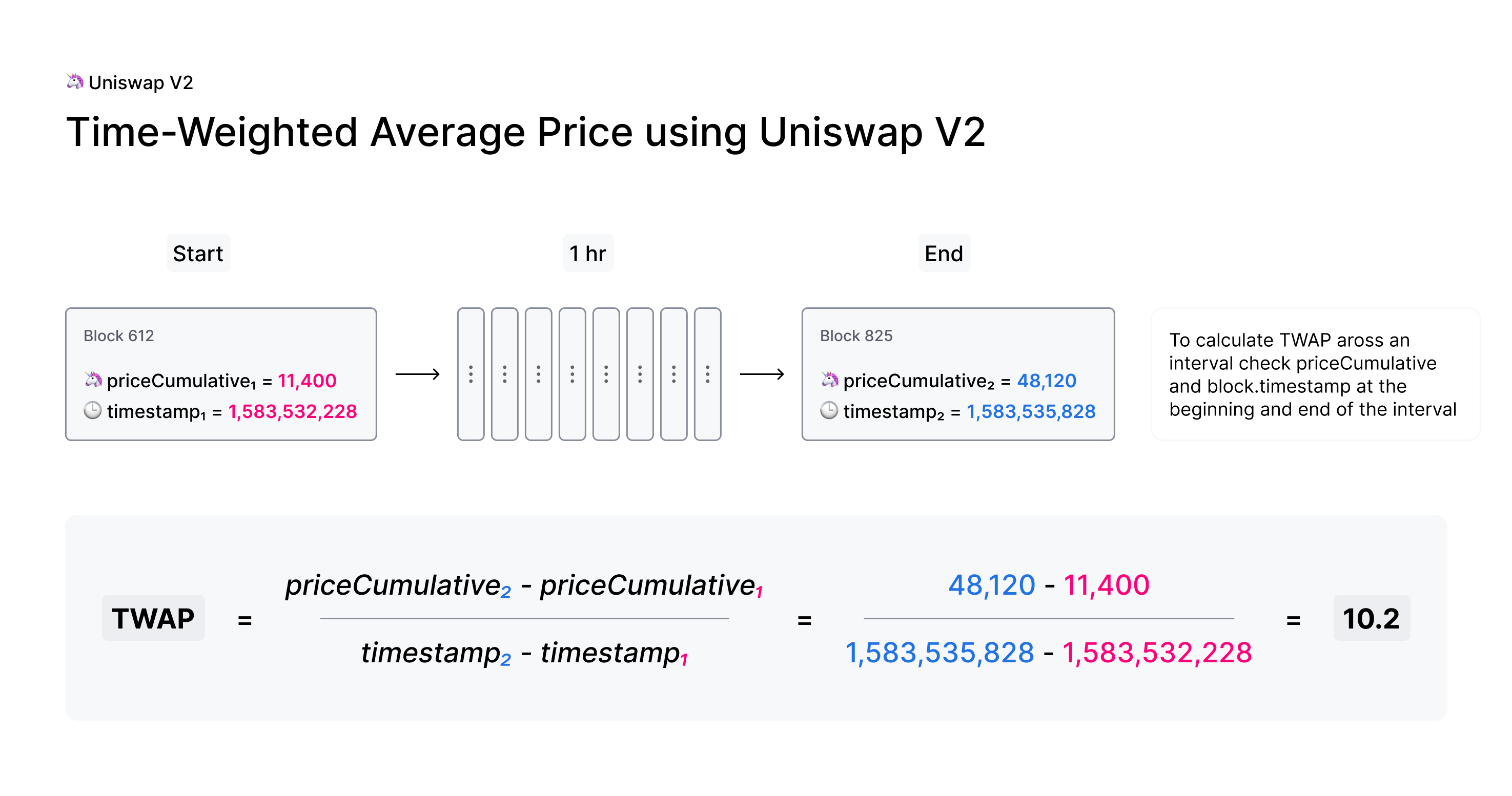
TWAP works by averaging a price for a token in a pool over a set period of time, making manipulating prices extremely difficult. Each new block pairs measure the market price before trades take place.

Let’s say we wish to measure the TWAP of a token price over a set of time T. The equation to find the TWAP price is calculated by dividing the cumulative price (or the aforementioned priceCumulative variable in the pictures) by T.
This gives us an average price that is resilient to an outlier price given by the oracle. For example, if a token were to be manipulated at block 10 with an outrageous price, instead of drawing this inaccurate reading to be the true price of swap, it is averaged between blocks 6, 7, 8, and 9 which read much closer to the accurate price. Therefore, much less slippage/manipulation is realized by the end user.
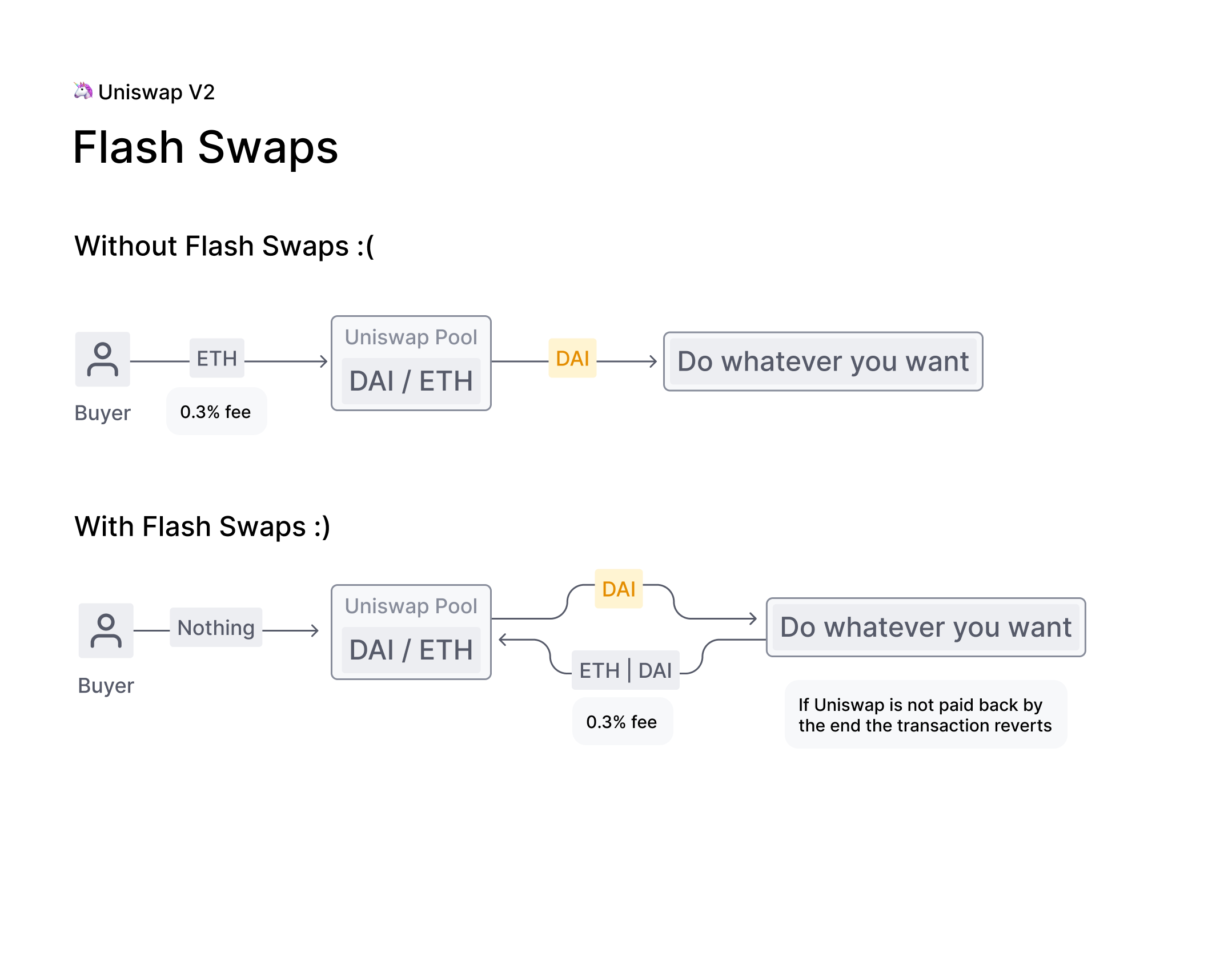
Flash Swaps :
Uniswap V2 flash swaps allow you to withdraw as much as you want of any ERC20 token on Uniswap at no upfront cost and do anything you want with them (execute arbitrary code), provided that by the end of the transaction execution, you either:
- Pay for all ERC20 tokens withdrawn
- Pay for a percentage of ERC20 tokens and return the rest
- Return all ERC20 tokens withdrawn
Liquidity provider fees are enforced by subtracting 0.3% from all input amounts, even if the input ERC20 tokens are being returned as part of a flash swap.
Uniswap V3
Uniswap V3 was launched on May 5, 2021 with numerous features among many others: concentrated liquidity, multiple fee tiers, non-fungible liquidity, and improved TWAP oracles.
- Concentrated liquidity : Giving individual LPs granular control over what price ranges their capital is allocated to. Individual positions are aggregated together into a single pool, forming one combined curve for users to trade against
- Multiple fee tiers : Allowing LPs to be appropriately compensated for taking on varying degrees of risk
- Non-fungible liquidity : As a byproduct of per-LP custom price curves, liquidity positions are no longer fungible and are not represented as ERC20 tokens in the core protocol.
- Improved TWAP Oracles : Uniswap v3 offers significant improvements to the TWAP oracle, making it possible to calculate any recent TWAP within the past ~9 days in a single on-chain call. This is achieved by storing an array of cumulative sums instead of just one.
- Improved TWAP Oracles : Uniswap v3 offers significant improvements to the TWAP oracle, making it possible to calculate any recent TWAP within the past ~9 days in a single on-chain call. This is achieved by storing an array of cumulative sums instead of just one.
References
Thank you <3